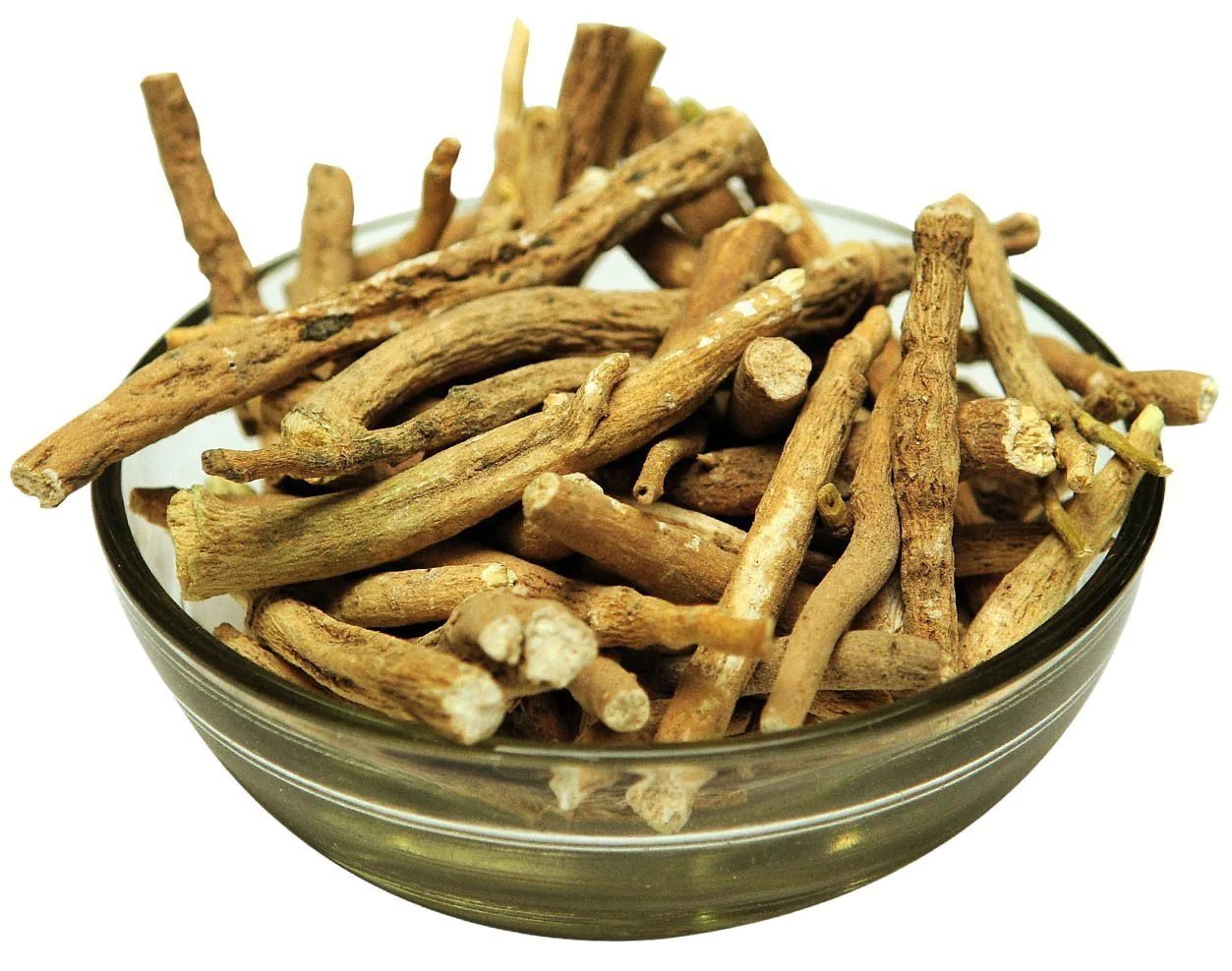
Ashwagandha is a staple of ayurvedic medicine and has been used for centuries as a way to relieve stress, restore calm and focus, and promote better sleep.
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen, a class plant-based medicines that help our bodies resist—or 'adapt'—to physical and chemical stressors in our environment.
Research suggests the secret to their power lies in their ability to 'hack' the body's stress-protection response, allowing us to maintain a comfortable level of stress during intense physical or mental stimulation.
According to several studies, Ashwagandha can effectively boost endurance while exercising; it also improves brain function and decreases body pain and muscular fatigue.
Things To Know About
- Stress. Taking Ashwagandha by mouth seems to help reduce stress in some people. It might also help reduce stress-related weight gain.
- Pregnancy: It is likely unsafe to use Ashwagandha when pregnant. There is some evidence that Ashwagandha might cause miscarriages.
- Breastfeeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if Ashwagandha is safe to use when breastfeeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
- "Auto-immune diseases" such as multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or other conditions: Ashwagandha might cause the immune system to become more active, and this could increase the symptoms of auto-immune diseases. If you have one of these conditions, it's best to avoid using Ashwagandha.
- Surgery: Ashwagandha may slow down the central nervous system. Healthcare providers worry that anesthesia and other medications during and after surgery might increase this effect. Stop taking Ashwagandha at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
- Thyroid disorders: Ashwagandha might increase thyroid hormone levels. Ashwagandha should be used cautiously or avoided if you have a thyroid condition or take thyroid hormone medications.
Be cautious with this combination
Medications that decrease the immune system (Immunosuppressants) interacts with ASHWAGANDHA
- Ashwagandha seems to increase the immune system. Taking ashwagandha along with medications that decrease the immune system might decrease the effectiveness of medications that decrease the immune system.
- Some medications that decrease the immune system include azathioprine (Imuran), basiliximab (Simulect), cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune), daclizumab (Zenapax), muromonab-CD3 (OKT3, Orthoclone OKT3), mycophenolate (CellCept), tacrolimus (FK506, Prograf), sirolimus (Rapamune), prednisone (Deltasone, Orasone), corticosteroids (glucocorticoids), and others.
Sedative medications (Benzodiazepines) interacts with ASHWAGANDHA
- Ashwagandha might cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Drugs that cause sleepiness and drowsiness are called sedatives. Taking ashwagandha along with sedative medications might cause too much sleepiness.
- Some of these sedative medications include clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), and others.
Sedative medications (CNS depressants) interacts with ASHWAGANDHA
- Ashwagandha might cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Medications that cause sleepiness are called sedatives. Taking ashwagandha along with sedative medications might cause too much sleepiness.
- Some sedative medications include clonazepam (Klonopin), lorazepam (Ativan), phenobarbital (Donnatal), zolpidem (Ambien), and others.
Minor Interaction
- Be watchful with this combination
Thyroid hormone interacts with ASHWAGANDHA
- The body naturally produces thyroid hormones. Ashwagandha might increase how much thyroid hormone the body produces. Taking ashwagandha with thyroid hormone pills might cause too much thyroid hormone in the body, and increase the effects and side effects of thyroid hormone.


Comments ()